SMM, December 27:
When silicon is fully lithiated, its volume expands by more than 300%, and this significant volume change brings a series of issues. 1) The volume effect causes high internal stress in the battery, which can easily compress the pole piece, leading to cracks and even pulverization of the silicon anode material. 2) The volume expansion effect makes the electrode material prone to losing contact with the current collector, causing the active material to detach from the pole piece, resulting in rapid capacity decay of the battery. 3) The volume expansion effect tends to form an unstable solid electrolyte interphase (SEI) film. Due to the volume change of silicon, the SEI film breaks, exposing new silicon surfaces that generate new SEI films, continuously consuming lithium ions in the electrolyte. This leads to irreversible capacity loss and low initial charge efficiency. Additionally, the SEI thickness increases with electrochemical cycling, and an excessively thick SEI layer hinders electron transfer and Li+ ion diffusion, increasing impedance.
Furthermore, as the silicon content increases, the initial Coulombic efficiency decreases. The initial irreversible cycle loss of silicon materials can reach up to 30% (compared to 5-10% for graphite). Side reactions between the electrolyte solvent and lithium chemicals form a solid electrolyte interphase (SEI) film on the anode of the lithium-ion battery, consuming lithium. Volume changes prevent the SEI from stably forming on the Si electrode surface, causing repeated SEI breakage and consuming a large amount of Li+ ions. Meanwhile, the SEI thickness increases with electrochemical cycling, and an excessively thick SEI layer hinders electron transfer and Li+ ion diffusion, increasing impedance and polarization.
Solutions to the issues of silicon-based anodes:
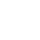
(1) Nanostructuring
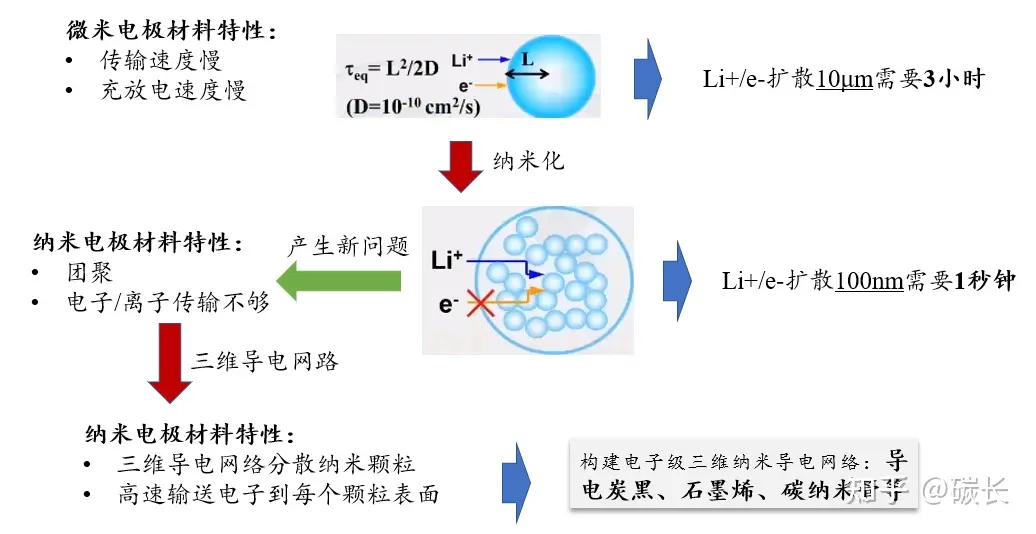
(2) Coating
Reducing particle size increases surface energy, and the surface energy of nanoparticles rises, weakening stability and causing the electrolyte to preferentially decompose (reduction/oxidation) with the nanoparticles.
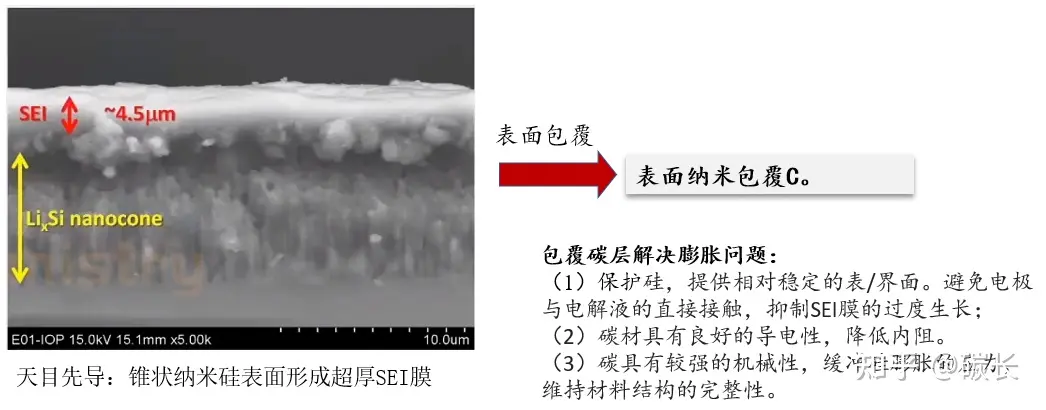
(3) Compromise solution -- Silicon monoxide anode
(Image source: Internet)
SMM New Energy Research Team
Cong Wang 021-51666838
Xiaodan Yu 021-20707870
Rui Ma 021-51595780
Ying Xu 021-51666707
Disheng Feng 021-51666714
Yujun Liu 021-20707895
Yanlin Lü 021-20707875
Zhicheng Zhou 021-51666711
Haohan Zhang 021-51666752
Zihan Wang 021-51666914
Xiaoxuan Ren 021-20707866
Yushuo Liang 021-20707892
Jie Wang 021-51595902
Yang Xu 021-51666760
Mengqi Xu 021-20707868