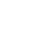
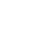
According to SMM data, China's magnesium ingot production in December 2024 decreased by 6.4% MoM.

In the magnesium ingot market this month, some smelting enterprises increased production while others implemented production cuts. The main reason for the production decline was the dual impact of supply surplus and weak demand, which caused magnesium ingot prices to continuously drop over the past two months. When prices fell below the break-even point for smelting enterprises, they were forced to cut production or halt operations. Meanwhile, the reasons for production increases included two factors: first, smelting enterprises that had previously suspended production due to maintenance gradually resumed operations, leading to increased supply. Second, some enterprises adjusted daily production based on orders and inventory levels, resulting in higher output.
According to SMM, the reduction and suspension of production in major magnesium-producing regions continued in December. Affected by weak demand, magnesium ingot smelting enterprises in these regions faced losses across the entire production cycle. Some announced official production cuts, and due to the cold winter weather, it was difficult for previously suspended producers to resume operations in the short term. Magnesium ingot supply maintained a downward trend, and information from major production regions indicated that current inventories at manufacturers had dropped to safe levels. On the demand side, weak material prices for magnesium ingots led to strong wait-and-see sentiment among downstream enterprises, resulting in cautious purchasing attitudes. From the perspective of supply and demand, magnesium ingot supply remained relatively ample, and short-term magnesium prices are expected to remain stable.