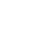
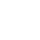
In October 2024, SMM reported that blister copper RCs in south China were quoted at 650-850 yuan/mt, with an average of 750 yuan/mt, down 50 yuan/mt MoM. In north China, blister copper RCs were quoted at 900-1,100 yuan/mt, with an average of 1,000 yuan/mt, unchanged from the previous month. CIF imported blister copper RCs were quoted at $100-120/mt, with an average of $110/mt, also unchanged from the previous month.
In October, domestic blister copper RCs remained at low levels, and market tension did not ease. Supply side, copper prices fluctuated, rising first and then falling, but overall fluctuations were minor. The supply of copper scrap did not show significant growth, and the specific implementation plan of Document No. 783 was not yet clear. Additionally, the tight supply of copper concentrates persisted, leading to an overall shortage in the blister copper market. Demand side, raw material inventories at smelters gradually decreased, and as year-end approaches, plants actively pursued their targets. Moreover, compared to using blister copper and copper anode, the losses from using spot copper concentrates for production were greater this year, further driving demand for blister copper and copper anode. On the import side, spot mined copper anode remained scarce, and copper anode imports were at low levels this year.
However, entering November, the tight situation in the blister copper market is expected to ease, and domestic blister copper RCs are finally rebounding.
Last week, SMM reported that blister copper RCs in south China were quoted at 1,000-1,200 yuan/mt, with an average of 1,100 yuan/mt, up 350 yuan/mt WoW. In north China, blister copper RCs were quoted at 900-1,100 yuan/mt, with an average of 1,000 yuan/mt, unchanged WoW. CIF imported blister copper RCs were quoted at $100-120/mt, with an average of $110/mt, unchanged WoW. Domestic copper anode RCs were quoted at 500-600 yuan/mt, with an average of 550 yuan/mt, up 100 yuan/mt WoW.
The easing of market pressure in November is mainly due to reduced demand. A major smelter is undergoing maintenance in the smelting process, which will significantly reduce its blister copper procurement, thereby pushing up blister copper RCs in surrounding areas. However, since the smelter's refining process is still operating normally, demand for copper anode is rising to ensure copper cathode production. Meanwhile, the supply of copper anode is unlikely to increase significantly in the short term, so the rise in copper anode RCs is relatively small compared to blister copper.